
Digestive Health
By Dr Saravana K.


Risk factors for H. pylori infection are related to living conditions in your childhood, such as living in crowded conditions, without a reliable supply of clean water, unsanitary living conditions and living with someone who has an H. pylori infection.
Symptoms
Most people will never have any signs or symptoms. When signs or symptoms do occur with H. pylori infection, they may include: an ache or burning pain in your abdomen, abdominal pain that’s worse when your stomach is empty, nausea, loss of appetite, bloating and unintentional weight loss.
Complications
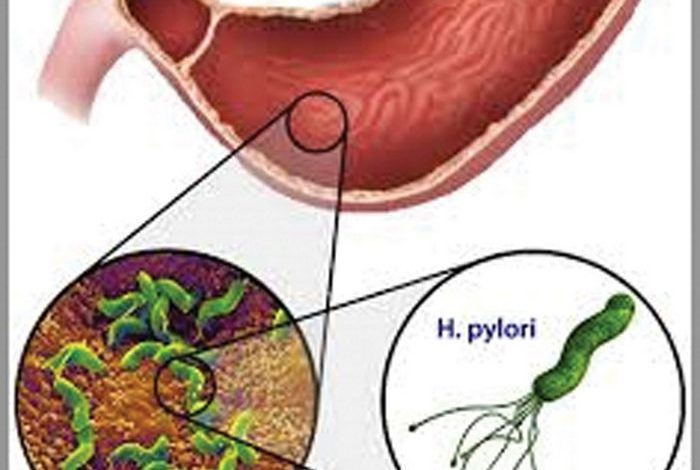
- Ulcers. H. pylori can damage the protective lining of your stomach and small intestine. This can allow stomach acid to create an open sore (ulcer). About 10 per cent of people with H. pylori will develop an ulcer.
- Inflammation of the stomach lining. H. pylori infection can irritate your stomach, causing inflammation (gastritis).
- Stomach cancer. H. pylori infection is a risk factor for certain types of stomach cancer.
Tests and procedures used to determine whether you have an H. pylori infection include:
- Blood test. Analysis of a blood sample may reveal evidence of an active or previous H. pylori infection in your body. However, breath and stool tests are better at detecting active H. pylori infections than is a blood test.
- Breath test. During a breath test, you swallow a pill, liquid or pudding that contains tagged carbon molecules. If you have an H. pylori infection, carbon is released when the solution is broken down in your stomach.
- Your body absorbs the carbon and expels it when you exhale. You exhale into a bag, and your doctor uses a special device to detect the carbon molecules. Acid-suppressing drugs known as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) and antibiotics can interfere with the accuracy of this test. You will need to stop taking those medications for a week or two weeks before you have the test. This test is available for adults and children.
- Scope test. You’ll be sedated for this test, known as an endoscopy exam. During the exam, your doctor threads a long flexible tube equipped with a tiny camera (endoscope) down your throat and esophagus and into your stomach and duodenum.
- This instrument allows your doctor to view any irregularities in your upper digestive tract including cancer and remove tissue samples (biopsy). These samples are analyzed for H. pylori infection.
Treatment
H. pylori infections are usually treated with two varieties of antibiotics at once, to help prevent the bacteria from developing a resistance to one particular antibiotic. An acid-suppressing drug, to help your stomach lining heal would also be prescribed.
You would need to undergo testing for H. pylori at least four weeks after your treatment. If the tests show the treatment was unsuccessful, you may undergo another round of treatment with a different combination of antibiotic medications.


