
Digestive Health
By Dr Saravana.K
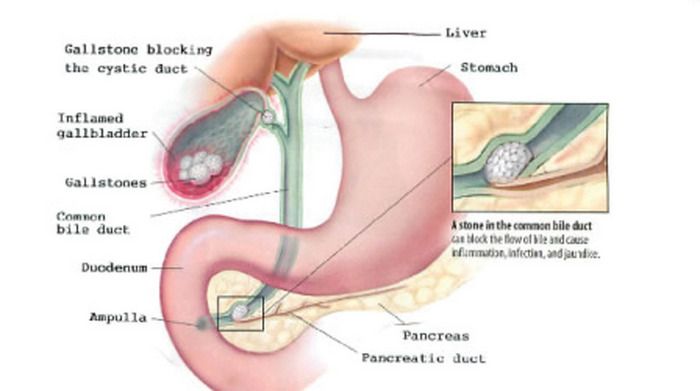
Gallstones are stone-like objects that form in the gallbladder or bile ducts. Gallbladder is an organ that resembles a small pear, located under the liver on the right side of the abdomen. The function is to store and dispense bile, a fluid that is produced by the liver and helps digest fats in the foods you eat.
It is connected to the liver and the intestine by a group of ducts, including the hepatic duct, the cystic duct, and the common bile duct. When you eat, the gallbladder sends bile through the common bile duct into the intestine to help you digest food.
There are two types of gallstones:
Cholesterol gallstones can form when there is too much cholesterol or bilirubin in the bile.
Pigment gallstones may form in people who have certain blood disorders.


Who is at risk for gallstones?
- women
- over the age of 40
- who have a family history of gallstones
- obese
- diabetes
- people whose diet is high in fat and cholesterol
In many cases, people who have gallstones do not have any symptoms.
The main symptom of gallstones is pain which can occur when gallstones move from the gallbladder into one of the ducts. Gallstones that migrate can cause conditions such as acute cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder), cholangitis (infection and inflammation of the bile ducts), and pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
The pain may be located in the upper part of the abdomen, between the shoulder blades, or under the right shoulder.
The most commonly used test to detect gallstones is ultrasound.
Other tests that may help in the diagnosis of gallstones include the following:
CT scan
endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) – a flexible tube with a light and a camera attached – is inserted into the patient’s mouth, down the throat, and into the stomach and small intestine. A dye is injected to allow the bile ducts to stand out. If there are gallstones in the bile duct, they can be removed by the endoscope.
magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography
endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) a small ultrasound transducer is installed on the tip of an endoscope and inserted into the patient’s mouth to obtain images of the biliary system
If you have no symptoms, you probably do not need treatment.
If you have symptoms, laparoscopic surgery is done to remove the gallbladder.
If there are gallstones in the bile duct, they need to be removed, most commonly with the ERCP.
Can I digest food without a gallbladder?
You don’t need a gallbladder in order to digest food properly. Bile will flow directly from your liver through the hepatic duct and the common bile duct to the small intestine.
For more information call Saravana.K Gastroenterologist and Liver Specialist Clinic at Hospital Fatimah (05 548 7181) or email gastrosara@gmail.com.


