
Child Health
By Dr Shan Narayanan
A genetic disorder is an illness caused by abnormality of chromosome or genes. Some illnesses are partly due to genetics and factors in the environment.
Genetic disorders are grouped into three categories, Single gene disorders, Chromosomal disorders and Multifactorial inheritance disorders (genetic and environmental influence).
Single gene disorders are caused by a mutation in a single gene. Mutation means structure of the gene is altered. This alteration can be passed on to subsequent generations in the following ways: autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive and X-linked: In this article I will discuss about the autosomal dominant and recessive inheritance.


Autosomal genes occur in pairs, with one coming from each parent. In an illness inherited as autosomal dominant, the individual has an abnormal gene on one chromosome, paired with a normal gene on the other chromosome. Most of the time, the abnormal gene was inherited from one of the individual’s parents. At times, a new mutation happens in the affected individual and not be present in one of his parents. In individuals with an autosomal dominant illness, there is a 50% chance with each pregnancy that the abnormal gene will be passed on to a child. An example of autosomal dominantly inherited condition is polydactaly (having extra digits). Diagram 1 illustrates autosomal dominant inheritance.


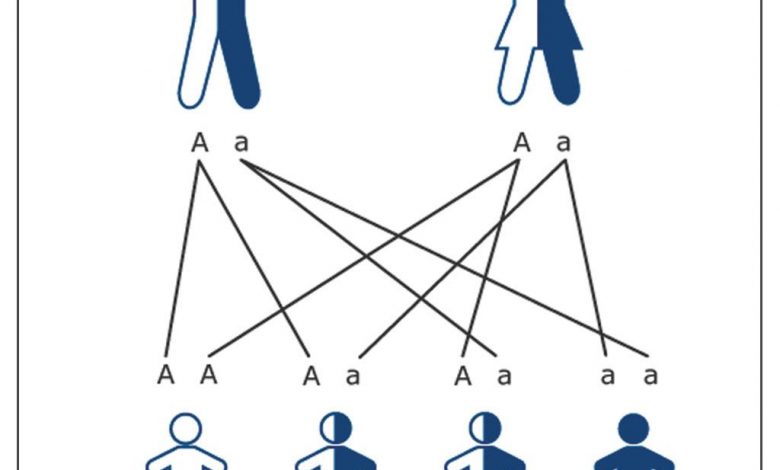
In an illness inherited as autosomal recessive, the individual has abnormal gene on both chromosomes. The abnormal genes were inherited one from each of the individual’s parents. If the child only inherits an abnormal gene from one parent pairing with a normal gene from the other parent, the child will be a “carrier”, but will not have symptoms (Diagram 2).
If two carriers of the same abnormal gene have children, there is a 25% chance with each pregnancy that the child will inherit two abnormal genes (one from each carrier parent), and these children will develop symptoms of the disease (Diagram 3). An example of autosomal recessive illness is Thalassemia.


Haemoglobin is composed of four polypeptide (protein) chains, which in adults consist of two alpha (a) globin chains and two beta (b) globin chains.
Individuals with thalassemia make less haemoglobin and thus they have less red blood cell cells. They thus have anaemia.
There are 2 types of thalassemia, alpha thalassemia (less alpha chains) and beta thalassemia (less beta chains).
I will discuss more on thalassemia in the next article.


